Tutorial 5 - Electric Aircraft Simulation#
Welcome to this tutorial on simulating an electric aircraft using RCAIDE. This guide will walk you through the code, explain its components, and highlight where modifications can be made to customize the simulation for different vehicle designs.
Header and Imports#
The Imports section is divided into two parts: simulation-specific libraries and general-purpose Python libraries.
The RCAIDE Imports section includes the core modules needed for the simulation. These libraries provide specialized classes and tools for building, analyzing, and running aircraft models.
[1]:
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# IMPORT
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# RCAIDE imports
import RCAIDE
from RCAIDE.Framework.Core import Units
from RCAIDE.Library.Methods.Powertrain.Propulsors.Electric_Rotor import design_electric_rotor
from RCAIDE.Library.Methods.Geometry.Planform import wing_segmented_planform
from RCAIDE.Library.Plots import *
# python imports
import numpy as np
from copy import deepcopy
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pickle
import sys
sys.path.insert(0,(os.path.dirname(os.getcwd())))
Vehicle Setup#
The ``vehicle_setup`` function defines the baseline configuration of the aircraft. This section builds the vehicle step-by-step by specifying its components, geometric properties, and high-level parameters.
1. Creating the Vehicle Instance#
The setup begins by creating a vehicle instance and assigning it a tag. The tag is a unique string identifier used to reference the vehicle during analysis or in post-processing steps.
2. Defining High-Level Vehicle Parameters#
The high-level parameters describe the aircraft’s key operational characteristics, such as:
Maximum Takeoff Weight: The heaviest allowable weight of the aircraft for safe flight.
Operating Empty Weight: The aircraft weight without fuel, passengers, or payload.
Payload: The weight of cargo and passengers.
Max Zero Fuel Weight: The maximum weight of the aircraft excluding fuel.
Units for these parameters can be converted automatically using the Units module to ensure consistency and reduce errors.
3. Defining the Landing Gear#
Landing gear parameters, such as the number of main and nose wheels, are set for the aircraft. While not used in this tutorial, these values can be applied in advanced analyses, such as ground loads or noise prediction.
4. Main Wing Setup#
The main wing is added using the ``Main_Wing`` class. This designation ensures that the primary lifting surface is recognized correctly by the analysis tools. Key properties of the wing include:
Area: The total wing surface area.
Span: The length of the wing from tip to tip.
Aspect Ratio: A ratio of span to average chord, determining wing efficiency.
Segments: Divisions of the wing geometry (e.g., root and tip sections).
Control Surfaces: High-lift devices like flaps and ailerons, defined by span fractions and deflections.
5. Horizontal and Vertical Stabilizers#
The stabilizers provide stability and control for the aircraft:
Horizontal Stabilizer: Defined using the
Horizontal_Tailclass. It follows a similar setup to the main wing but acts as a stabilizing surface.Vertical Stabilizer: Defined using the
Vertical_Tailclass, with an additional option to designate the tail as a T-tail for weight calculations.
6. Fuselage Definition#
The fuselage is modeled by specifying its geometric parameters, such as:
Length: The overall length of the aircraft body.
Width: The widest part of the fuselage cross-section.
Height: The height of the fuselage.
These values influence drag calculations and overall structural weight.
7. Energy Network#
The energy network models the propulsion system. The energy network determines the engine’s thrust, bypass ratio, and fuel type. These parameters are essential for performance and fuel efficiency analyses.
[2]:
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Build the Vehicle
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
def vehicle_setup():
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# ################################################# Vehicle-level Properties ########################################################
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
vehicle = RCAIDE.Vehicle()
vehicle.tag = 'X57_Maxwell_Mod2'
vehicle.mass_properties.max_takeoff = 2712. * Units.pounds
vehicle.mass_properties.takeoff = 2712. * Units.pounds
vehicle.mass_properties.max_zero_fuel = 2712. * Units.pounds
vehicle.mass_properties.max_payload = 50. * Units.pounds #
vehicle.flight_envelope.ultimate_load = 3.75
vehicle.flight_envelope.positive_limit_load = 2.5
vehicle.flight_envelope.design_mach_number = 0.78
vehicle.flight_envelope.design_cruise_altitude = 2500. * Units.ft
vehicle.flight_envelope.design_range = 200 * Units.nmi
vehicle.flight_envelope.design_dynamic_pressure = 2072.1614727510914
vehicle.flight_envelope.design_mach_number = 0.17734782770792362
vehicle.reference_area = 14.76
vehicle.passengers = 4
vehicle.systems.control = "fully powered"
vehicle.systems.accessories = "commuter"
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# ######################################################## Wings ####################################################################
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
# Main Wing
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
wing = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Wings.Main_Wing()
wing.tag = 'main_wing'
wing.sweeps.quarter_chord = 0.0 * Units.deg
wing.thickness_to_chord = 0.12
wing.areas.reference = 14.76
wing.spans.projected = 11.4
wing.chords.root = 1.46
wing.chords.tip = 0.92
wing.chords.mean_aerodynamic = 1.19
wing.taper = wing.chords.root/wing.chords.tip
wing.aspect_ratio = wing.spans.projected**2. / wing.areas.reference
wing.twists.root = 3.0 * Units.degrees
wing.twists.tip = 0.0 * Units.degrees
wing.origin = [[2.93, 0., 1.01]]
wing.aerodynamic_center = [3., 0., 1.01]
wing.vertical = False
wing.symmetric = True
wing.high_lift = True
wing.winglet_fraction = 0.0
wing.dynamic_pressure_ratio = 1.0
ospath = os.path.abspath(os.path.join('Notebook'))
separator = os.path.sep
rel_path = os.path.dirname(ospath) + separator + '..' + separator + '..' + separator + 'VnV' + separator + 'Vehicles' + separator
airfoil = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Airfoils.Airfoil()
airfoil.tag = 'NACA_63_412.txt'
airfoil.coordinate_file = rel_path + 'Airfoils' + separator + 'NACA_63_412.txt' # absolute path
cg_x = wing.origin[0][0] + 0.25*wing.chords.mean_aerodynamic
cg_z = wing.origin[0][2] - 0.2*wing.chords.mean_aerodynamic
vehicle.mass_properties.center_of_gravity = [[cg_x, 0. , cg_z ]] # SOURCE: Design and aerodynamic analysis of a twin-engine commuter aircraft
# Wing Segments
segment = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Wings.Segments.Segment()
segment.tag = 'inboard'
segment.percent_span_location = 0.0
segment.twist = 3. * Units.degrees
segment.root_chord_percent = 1.
segment.dihedral_outboard = 0.
segment.sweeps.quarter_chord = 0.
segment.thickness_to_chord = 0.12
segment.append_airfoil(airfoil)
wing.append_segment(segment)
segment = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Wings.Segments.Segment()
segment.tag = 'outboard'
segment.percent_span_location = 0.5438
segment.twist = 2.* Units.degrees
segment.root_chord_percent = 1.
segment.dihedral_outboard = 0.
segment.sweeps.quarter_chord = 0.
segment.thickness_to_chord = 0.12
segment.append_airfoil(airfoil)
wing.append_segment(segment)
# Wing Segments
segment = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Wings.Segments.Segment()
segment.tag = 'winglet'
segment.percent_span_location = 0.98
segment.twist = 1. * Units.degrees
segment.root_chord_percent = 0.630
segment.dihedral_outboard = 75. * Units.degrees
segment.sweeps.quarter_chord = 30. * Units.degrees
segment.thickness_to_chord = 0.12
segment.append_airfoil(airfoil)
wing.append_segment(segment)
segment = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Wings.Segments.Segment()
segment.tag = 'tip'
segment.percent_span_location = 1.
segment.twist = 0. * Units.degrees
segment.root_chord_percent = 0.12
segment.dihedral_outboard = 0.
segment.sweeps.quarter_chord = 0.
segment.thickness_to_chord = 0.12
segment.append_airfoil(airfoil)
wing.append_segment(segment)
# Fill out more segment properties automatically
wing = wing_segmented_planform(wing)
# add to vehicle
vehicle.append_component(wing)
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Horizontal Tail
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
wing = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Wings.Horizontal_Tail()
wing.tag = 'horizontal_stabilizer'
wing.sweeps.quarter_chord = 0.0 * Units.deg
wing.thickness_to_chord = 0.12
wing.areas.reference = 2.540
wing.spans.projected = 3.3 * Units.meter
wing.sweeps.quarter_chord = 0 * Units.deg
wing.chords.root = 0.769 * Units.meter
wing.chords.tip = 0.769 * Units.meter
wing.chords.mean_aerodynamic = 0.769 * Units.meter
wing.taper = 1.
wing.aspect_ratio = wing.spans.projected**2. / wing.areas.reference
wing.twists.root = 0.0 * Units.degrees
wing.twists.tip = 0.0 * Units.degrees
wing.origin = [[7.7, 0., 0.25]]
wing.aerodynamic_center = [7.8, 0., 0.25]
wing.vertical = False
wing.winglet_fraction = 0.0
wing.symmetric = True
wing.high_lift = False
wing.dynamic_pressure_ratio = 0.9
# add to vehicle
vehicle.append_component(wing)
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Vertical Stabilizer
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
wing = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Wings.Vertical_Tail()
wing.tag = 'vertical_stabilizer'
wing.sweeps.quarter_chord = 25. * Units.deg
wing.thickness_to_chord = 0.12
wing.areas.reference = 2.258 * Units['meters**2']
wing.spans.projected = 1.854 * Units.meter
wing.chords.root = 1.6764 * Units.meter
wing.chords.tip = 0.6858 * Units.meter
wing.chords.mean_aerodynamic = 1.21 * Units.meter
wing.taper = wing.chords.tip/wing.chords.root
wing.aspect_ratio = wing.spans.projected**2. / wing.areas.reference
wing.twists.root = 0.0 * Units.degrees
wing.twists.tip = 0.0 * Units.degrees
wing.origin = [[6.75 ,0, 0.623]]
wing.aerodynamic_center = [0.508 ,0,0]
wing.vertical = True
wing.symmetric = False
wing.t_tail = False
wing.winglet_fraction = 0.0
wing.dynamic_pressure_ratio = 1.0
# add to vehicle
vehicle.append_component(wing)
# ########################################################## Fuselage ############################################################
fuselage = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Fuselages.Tube_Fuselage()
# define cabin
cabin = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Fuselages.Cabins.Cabin()
economy_class = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Fuselages.Cabins.Classes.Economy()
economy_class.number_of_seats_abrest = 2
economy_class.number_of_rows = 3
economy_class.galley_lavatory_percent_x_locations = []
economy_class.emergency_exit_percent_x_locations = []
economy_class.type_A_exit_percent_x_locations = []
cabin.append_cabin_class(economy_class)
fuselage.append_cabin(cabin)
fuselage.fineness.nose = 1.6
fuselage.fineness.tail = 2.
fuselage.lengths.nose = 60. * Units.inches
fuselage.lengths.tail = 161. * Units.inches
fuselage.lengths.cabin = 105. * Units.inches
fuselage.lengths.total = 332.2* Units.inches
fuselage.width = 42. * Units.inches
fuselage.heights.maximum = 62. * Units.inches
fuselage.heights.at_quarter_length = 62. * Units.inches
fuselage.heights.at_three_quarters_length = 62. * Units.inches
fuselage.heights.at_wing_root_quarter_chord = 23. * Units.inches
fuselage.areas.side_projected = 8000. * Units.inches**2.
fuselage.areas.wetted = 30000. * Units.inches**2.
fuselage.areas.front_projected = 42.* 62. * Units.inches**2.
fuselage.effective_diameter = 50. * Units.inches
# Segment
segment = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Fuselages.Segments.Segment()
segment.tag = 'segment_0'
segment.percent_x_location = 0
segment.percent_z_location = 0
segment.height = 0.01
segment.width = 0.01
fuselage.segments.append(segment)
# Segment
segment = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Fuselages.Segments.Segment()
segment.tag = 'segment_1'
segment.percent_x_location = 0.007279116466
segment.percent_z_location = 0.002502014453
segment.height = 0.1669064748
segment.width = 0.2780205877
fuselage.segments.append(segment)
# Segment
segment = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Fuselages.Segments.Segment()
segment.tag = 'segment_2'
segment.percent_x_location = 0.01941097724
segment.percent_z_location = 0.001216095397
segment.height = 0.3129496403
segment.width = 0.4365777215
fuselage.segments.append(segment)
# Segment
segment = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Fuselages.Segments.Segment()
segment.tag = 'segment_3'
segment.percent_x_location = 0.06308567604
segment.percent_z_location = 0.007395489231
segment.height = 0.5841726619
segment.width = 0.6735119903
fuselage.segments.append(segment)
# Segment
segment = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Fuselages.Segments.Segment()
segment.tag = 'segment_4'
segment.percent_x_location = 0.1653761217
segment.percent_z_location = 0.02891281352
segment.height = 1.064028777
segment.width = 1.067200529
fuselage.segments.append(segment)
# Segment
segment = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Fuselages.Segments.Segment()
segment.tag = 'segment_5'
segment.percent_x_location = 0.2426372155
segment.percent_z_location = 0.04214148761
segment.height = 1.293766653
segment.width = 1.183058255
fuselage.segments.append(segment)
# Segment
segment = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Fuselages.Segments.Segment()
segment.tag = 'segment_6'
segment.percent_x_location = 0.2960174029
segment.percent_z_location = 0.04705241831
segment.height = 1.377026712
segment.width = 1.181540054
fuselage.segments.append(segment)
# Segment
segment = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Fuselages.Segments.Segment()
segment.tag = 'segment_7'
segment.percent_x_location = 0.3809404284
segment.percent_z_location = 0.05313580461
segment.height = 1.439568345
segment.width = 1.178218989
fuselage.segments.append(segment)
# Segment
segment = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Fuselages.Segments.Segment()
segment.tag = 'segment_8'
segment.percent_x_location = 0.5046854083
segment.percent_z_location = 0.04655492473
segment.height = 1.29352518
segment.width = 1.054390707
fuselage.segments.append(segment)
# Segment
segment = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Fuselages.Segments.Segment()
segment.tag = 'segment_9'
segment.percent_x_location = 0.6454149933
segment.percent_z_location = 0.03741966266
segment.height = 0.8971223022
segment.width = 0.8501926505
fuselage.segments.append(segment)
# Segment
segment = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Fuselages.Segments.Segment()
segment.tag = 'segment_10'
segment.percent_x_location = 0.985107095
segment.percent_z_location = 0.04540283436
segment.height = 0.2920863309
segment.width = 0.2012565415
fuselage.segments.append(segment)
# Segment
segment = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Fuselages.Segments.Segment()
segment.tag = 'segment_11'
segment.percent_x_location = 1
segment.percent_z_location = 0.04787575562
segment.height = 0.1251798561
segment.width = 0.1206021048
fuselage.segments.append(segment)
# add to vehicle
vehicle.append_component(fuselage)
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Electric Network
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
net = RCAIDE.Framework.Networks.Electric()
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Bus
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
bus = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Powertrain.Distributors.Electrical_Bus()
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Battery
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
bat = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Powertrain.Sources.Battery_Modules.Lithium_Ion_NMC()
bat.tag = 'li_ion_battery'
bat.electrical_configuration.series = 16
bat.electrical_configuration.parallel = 40
bat.geometrtic_configuration.normal_count = 20
bat.geometrtic_configuration.parallel_count = 32
for _ in range(8):
bus.battery_modules.append(deepcopy(bat))
bus.initialize_bus_properties()
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Starboard Propulsor
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
starboard_propulsor = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Powertrain.Propulsors.Electric_Rotor()
starboard_propulsor.tag = 'starboard_propulsor'
starboard_propulsor.origin = [[2., 2.5, 0.95]]
# Electronic Speed Controller
esc = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Powertrain.Modulators.Electronic_Speed_Controller()
esc.tag = 'esc_1'
esc.efficiency = 0.95
esc.bus_voltage = bus.voltage
starboard_propulsor.electronic_speed_controller = esc
# Propeller
propeller = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Powertrain.Converters.Propeller()
propeller.tag = 'propeller_1'
propeller.tip_radius = 1.72/2
propeller.number_of_blades = 3
propeller.hub_radius = 10. * Units.inches
propeller.cruise.design_freestream_velocity = 175.*Units['mph']
propeller.cruise.design_angular_velocity = 2700. * Units.rpm
propeller.cruise.design_Cl = 0.7
propeller.cruise.design_altitude = 2500. * Units.feet
propeller.cruise.design_thrust = 2000
propeller.clockwise_rotation = False
propeller.variable_pitch = True
propeller.origin = [[2.,2.5,0.95]]
airfoil = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Airfoils.Airfoil()
airfoil.tag = 'NACA_4412'
airfoil.coordinate_file = rel_path + 'Airfoils' + separator + 'NACA_4412.txt' # absolute path
airfoil.polar_files =[ rel_path + 'Airfoils' + separator + 'Polars' + separator + 'NACA_4412_polar_Re_50000.txt',
rel_path + 'Airfoils' + separator + 'Polars' + separator + 'NACA_4412_polar_Re_100000.txt',
rel_path + 'Airfoils' + separator + 'Polars' + separator + 'NACA_4412_polar_Re_200000.txt',
rel_path + 'Airfoils' + separator + 'Polars' + separator + 'NACA_4412_polar_Re_500000.txt',
rel_path + 'Airfoils' + separator + 'Polars' + separator + 'NACA_4412_polar_Re_1000000.txt']
propeller.append_airfoil(airfoil)
propeller.airfoil_polar_stations = [0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]
starboard_propulsor.rotor = propeller
# DC_Motor
motor = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Powertrain.Converters.DC_Motor()
motor.efficiency = 0.98
motor.origin = [[2., 2.5, 0.95]]
motor.nominal_voltage = bus.voltage * 0.5
motor.no_load_current = 1.0
starboard_propulsor.motor = motor
# design starboard propulsor
design_electric_rotor(starboard_propulsor)
# ########################################################## Nacelles ############################################################
nacelle = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Nacelles.Stack_Nacelle()
nacelle.tag = 'nacelle_1'
nacelle.length = 2
nacelle.diameter = 42 * Units.inches
nacelle.areas.wetted = 0.01*(2*np.pi*0.01/2)
nacelle.origin = [[2.5,2.5,1.0]]
nacelle.flow_through = False
nac_segment = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Nacelles.Segments.Segment()
nac_segment.tag = 'segment_1'
nac_segment.percent_x_location = 0.0
nac_segment.height = 0.0
nac_segment.width = 0.0
nacelle.append_segment(nac_segment)
nac_segment = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Nacelles.Segments.Segment()
nac_segment.tag = 'segment_2'
nac_segment.percent_x_location = 0.1
nac_segment.height = 0.5
nac_segment.width = 0.65
nacelle.append_segment(nac_segment)
nac_segment = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Nacelles.Segments.Segment()
nac_segment.tag = 'segment_3'
nac_segment.percent_x_location = 0.3
nac_segment.height = 0.52
nac_segment.width = 0.7
nacelle.append_segment(nac_segment)
nac_segment = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Nacelles.Segments.Segment()
nac_segment.tag = 'segment_4'
nac_segment.percent_x_location = 0.5
nac_segment.height = 0.5
nac_segment.width = 0.65
nacelle.append_segment(nac_segment)
nac_segment = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Nacelles.Segments.Segment()
nac_segment.tag = 'segment_5'
nac_segment.percent_x_location = 0.7
nac_segment.height = 0.4
nac_segment.width = 0.6
nacelle.append_segment(nac_segment)
nac_segment = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Nacelles.Segments.Segment()
nac_segment.tag = 'segment_6'
nac_segment.percent_x_location = 0.9
nac_segment.height = 0.3
nac_segment.width = 0.5
nacelle.append_segment(nac_segment)
nac_segment = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Nacelles.Segments.Segment()
nac_segment.tag = 'segment_7'
nac_segment.percent_x_location = 1.0
nac_segment.height = 0.0
nac_segment.width = 0.0
nacelle.append_segment(nac_segment)
starboard_propulsor.nacelle = nacelle
# append propulsor to distribution line
net.propulsors.append(starboard_propulsor)
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Port Propulsor
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
port_propulsor = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Powertrain.Propulsors.Electric_Rotor()
port_propulsor.tag = "port_propulsor"
port_propulsor.origin = [[2., -2.5, 0.95]]
esc_2 = deepcopy(esc)
esc_2.origin = [[2., -2.5, 0.95]]
port_propulsor.electronic_speed_controller = esc_2
propeller_2 = deepcopy(propeller)
propeller_2.tag = 'propeller_2'
propeller_2.origin = [[2.,-2.5,0.95]]
propeller_2.clockwise_rotation = False
port_propulsor.rotor = propeller_2
motor_2 = deepcopy(motor)
motor_2.origin = [[2., -2.5, 0.95]]
port_propulsor.motor = motor_2
nacelle_2 = deepcopy(nacelle)
nacelle_2.tag = 'nacelle_2'
nacelle_2.origin = [[2.5,-2.5,1.0]]
port_propulsor.nacelle = nacelle_2
# append propulsor to distribution line
net.propulsors.append(port_propulsor)
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Payload
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
payload = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Payloads.Payload()
payload.power_draw = 10. # Watts
payload.mass_properties.mass = 1.0 * Units.kg
bus.payload = payload
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Avionics
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
avionics = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Powertrain.Systems.Avionics()
avionics.power_draw = 20. # Watts
bus.avionics = avionics
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Assign propulsors to bus
bus.assigned_propulsors = [[starboard_propulsor.tag, port_propulsor.tag]]
# append bus
net.busses.append(bus)
vehicle.append_energy_network(net)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
# Vehicle Definition Complete
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
return vehicle
Configurations Setup#
The ``configs_setup`` function defines the different vehicle configurations (referred to as configs) used during the simulation. Configurations allow for modifications to the baseline vehicle, such as altering control surface settings, without redefining the entire vehicle.
1. Base Configuration#
The base configuration serves as the foundation for all other configurations. It is defined to match the baseline vehicle created in the vehicle_setup function. Configurations in RCAIDE are created as containers using RCAIDE Data classes. These classes provide additional functionality, such as the ability to append new configurations or modifications.
[3]:
def configs_setup(vehicle):
configs = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Configs.Config.Container()
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
# Initialize Configurations
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
base_config = RCAIDE.Library.Components.Configs.Config(vehicle)
base_config.tag = 'base'
configs.append(base_config)
# done!
return configs
Base Analysis#
The ``base_analysis`` function defines the analyses required for evaluating the aircraft. Each analysis addresses a specific aspect of the vehicle’s performance or characteristics. Below are the key analyses, their purpose, and considerations for their use.
1. Weights Analysis#
The weights analysis calculates the distribution of the aircraft’s weight across various components. This method is based on empirical correlations designed for tube-and-wing transport aircraft configurations.
Provides a breakdown of component weights (e.g., wings, fuselage, engines).
While informative, the results of this analysis are not directly used in the performance evaluation.
2. Aerodynamics Analysis#
The aerodynamics analysis evaluates the aerodynamic performance of the aircraft. It uses RCAIDE’s fidelity zero method:
Fidelity Zero: This is RCAIDE’s baseline aerodynamic analysis method, suitable for subsonic transport aircraft.
Similar to aerodynamic methods found in conceptual design texts.
Provides estimates for lift, drag, and other aerodynamic coefficients.
Note: Higher-fidelity aerodynamic methods are available for more detailed analyses if needed.
3. Stability Analysis#
The stability analysis calculates stability derivatives for the aircraft. While it is not used in the current mission setup, it can be run post-mission for checks or additional analysis.
Like the aerodynamic method, it uses fidelity zero for baseline stability analysis.
Applicable for basic stability checks of subsonic transport aircraft.
4. Energy Analysis#
The energy analysis runs the energy network attached to the vehicle. For this turboprop-powered aircraft:
The analysis evaluates the turboprop energy network.
Ensures the propulsion system behavior, such as thrust and fuel consumption, is accounted for.
5. Planet Analysis#
The planet analysis defines the planetary environment the vehicle operates in. This setup allows for the attachment of an atmospheric model.
6. Atmosphere Analysis#
The atmosphere analysis sets the atmospheric conditions for the simulation. A common choice is the US 1976 Standard Atmosphere, which provides:
Standard temperature, pressure, and density profiles with altitude.
Consistent atmospheric conditions for performance evaluations.
[4]:
def base_analysis(vehicle):
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
# Initialize the Analyses
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
analyses = RCAIDE.Framework.Analyses.Vehicle()
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
# Weights
weights = RCAIDE.Framework.Analyses.Weights.Electric()
weights.aircraft_type = 'General_Aviation'
weights.vehicle = vehicle
analyses.append(weights)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
# Aerodynamics Analysis
aerodynamics = RCAIDE.Framework.Analyses.Aerodynamics.Vortex_Lattice_Method()
aerodynamics.vehicle = vehicle
analyses.append(aerodynamics)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
# Energy
energy= RCAIDE.Framework.Analyses.Energy.Energy()
energy.vehicle = vehicle
analyses.append(energy)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
# Planet Analysis
planet = RCAIDE.Framework.Analyses.Planets.Earth()
analyses.append(planet)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
# Atmosphere Analysis
atmosphere = RCAIDE.Framework.Analyses.Atmospheric.US_Standard_1976()
atmosphere.features.planet = planet.features
analyses.append(atmosphere)
# done!
return analyses
Analyses Setup#
The ``analyses_setup`` function assigns a set of analyses to each vehicle configuration. Analyses are used to evaluate the aircraft’s performance, aerodynamics, energy systems, and other characteristics for a given configuration.
1. Overview of Analyses Assignment#
In this tutorial, all configurations share the same set of analyses. However, this function provides the flexibility to assign a unique set of analyses to any specific configuration.
2. Purpose of Analyses Assignment#
The analyses ensure that the defined vehicle configurations (e.g., cruise, takeoff, landing) are evaluated correctly during the simulation. Each configuration can have:
Common Analyses: Shared across multiple configurations for simplicity.
Custom Analyses: Tailored to a specific phase of flight or performance evaluation.
3. Typical Analyses Included#
The following analyses are typically assigned to each configuration:
Weights Analysis: Computes weight distribution across components.
Aerodynamics Analysis: Estimates lift, drag, and aerodynamic coefficients.
Stability Analysis: Evaluates stability derivatives for flight control assessments.
Energy Analysis: Runs the energy network (e.g., turboprop engine) for thrust and fuel performance.
Atmosphere Analysis: Sets atmospheric conditions using standard atmospheric models.
By assigning these analyses, the vehicle’s behavior under different configurations (e.g., cruise, takeoff, landing) can be comprehensively evaluated.
4. Customizing Analyses#
To assign a custom analysis set for a specific configuration:
Define a new analysis function tailored to the desired evaluation.
Replace the default analyses for the target configuration by calling the custom function.
For example, the takeoff configuration might use a modified aerodynamic analysis to account for flap and slat deployment.
[5]:
def analyses_setup(configs):
analyses = RCAIDE.Framework.Analyses.Analysis.Container()
# build a base analysis for each config
for tag,config in configs.items():
analysis = base_analysis(config)
analyses[tag] = analysis
return analyses
Mission Setup#
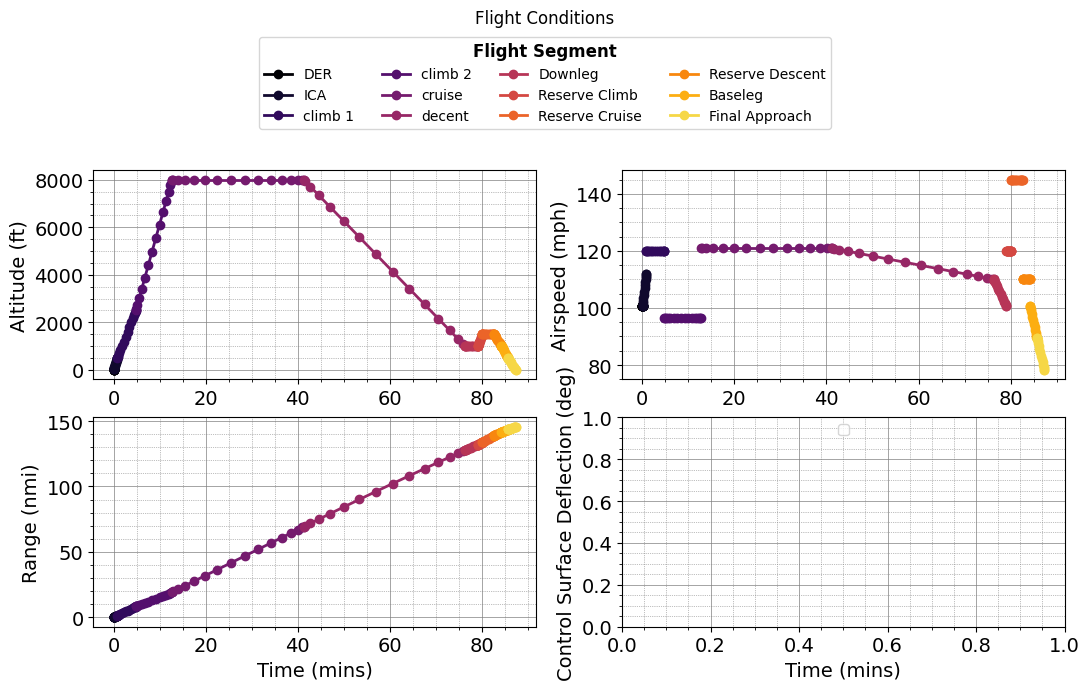
The ``mission_setup`` function defines the mission profile used to compute the aircraft’s performance. A mission profile consists of sequential segments that represent different phases of flight, such as climb, cruise, and descent.
1. Mission Profile Overview#
A mission profile is made up of individual flight segments. Each segment specifies the aircraft’s flight conditions, such as:
Altitude
Speed
Range
Time
These segments are simulated sequentially, allowing for a detailed performance analysis of the vehicle across all phases of flight.
2. Segments in the Mission Profile#
Common segments in a mission profile include:
Taxi: Ground movement of the aircraft before takeoff and after landing.
Takeoff: Acceleration and lift-off phase with high-lift devices deployed.
Climb: Gradual ascent to cruise altitude, often with reduced flap/slat deployment.
Cruise: Level flight at a constant altitude and speed for fuel-efficient operation.
Descent: Controlled reduction in altitude as the aircraft prepares for landing.
Landing: Final phase of flight with maximum flap and slat deployment for touchdown.
Each segment defines specific performance conditions and parameters, such as speed, altitude, and duration.
For more information on the mission solver and its implementation, refer to the relevant RCAIDE documentation.
[6]:
def mission_setup(analyses):
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
# Initialize the Mission
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
mission = RCAIDE.Framework.Mission.Sequential_Segments()
mission.tag = 'mission'
# unpack Segments module
Segments = RCAIDE.Framework.Mission.Segments
base_segment = Segments.Segment()
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
# Departure End of Runway Segment Flight 1 :
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
segment = Segments.Climb.Linear_Speed_Constant_Rate(base_segment)
segment.tag = 'DER'
segment.analyses.extend( analyses.base )
segment.altitude_start = 0.0 * Units.feet
segment.altitude_end = 50.0 * Units.feet
segment.air_speed_start = 45 * Units['m/s']
segment.air_speed_end = 45
segment.initial_battery_state_of_charge = 1
# define flight dynamics to model
segment.flight_dynamics.force_x = True
segment.flight_dynamics.force_z = True
# define flight controls
segment.assigned_control_variables.throttle.active = True
segment.assigned_control_variables.throttle.assigned_propulsors = [['starboard_propulsor','port_propulsor']]
segment.assigned_control_variables.body_angle.active = True
mission.append_segment(segment)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
# Initial Climb Area Segment Flight 1
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
segment = Segments.Climb.Linear_Speed_Constant_Rate(base_segment)
segment.tag = 'ICA'
segment.analyses.extend( analyses.base )
segment.altitude_start = 50.0 * Units.feet
segment.altitude_end = 500.0 * Units.feet
segment.air_speed_start = 45 * Units['m/s']
segment.air_speed_end = 50 * Units['m/s']
segment.climb_rate = 600 * Units['ft/min']
# define flight dynamics to model
segment.flight_dynamics.force_x = True
segment.flight_dynamics.force_z = True
# define flight controls
segment.assigned_control_variables.throttle.active = True
segment.assigned_control_variables.throttle.assigned_propulsors = [['starboard_propulsor','port_propulsor']]
segment.assigned_control_variables.body_angle.active = True
mission.append_segment(segment)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
# Climb Segment Flight 1
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
segment = Segments.Climb.Constant_Speed_Constant_Rate(base_segment)
segment.tag = 'climb_1'
segment.analyses.extend( analyses.base )
segment.altitude_start = 500.0 * Units.feet
segment.altitude_end = 2500 * Units.feet
segment.air_speed = 120 * Units['mph']
segment.climb_rate = 500* Units['ft/min']
# define flight dynamics to model
segment.flight_dynamics.force_x = True
segment.flight_dynamics.force_z = True
# define flight controls
segment.assigned_control_variables.throttle.active = True
segment.assigned_control_variables.throttle.assigned_propulsors = [['starboard_propulsor','port_propulsor']]
segment.assigned_control_variables.body_angle.active = True
mission.append_segment(segment)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
# Climb 1 : constant Speed, constant rate segment
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
segment = Segments.Climb.Constant_Speed_Constant_Rate(base_segment)
segment.tag = "climb_2"
segment.analyses.extend( analyses.base )
segment.altitude_start = 2500.0 * Units.feet
segment.altitude_end = 8012 * Units.feet
segment.air_speed = 96.4260 * Units['mph']
segment.climb_rate = 700.034 * Units['ft/min']
# define flight dynamics to model
segment.flight_dynamics.force_x = True
segment.flight_dynamics.force_z = True
# define flight controls
segment.assigned_control_variables.throttle.active = True
segment.assigned_control_variables.throttle.assigned_propulsors = [['starboard_propulsor','port_propulsor']]
segment.assigned_control_variables.body_angle.active = True
mission.append_segment(segment)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
# Cruise Segment: constant Speed, constant altitude
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
segment = Segments.Cruise.Constant_Speed_Constant_Altitude(base_segment)
segment.tag = "cruise"
segment.analyses.extend(analyses.base)
segment.altitude = 8012 * Units.feet
segment.air_speed = 120.91 * Units['mph']
segment.distance = 50. * Units.nautical_mile
# define flight dynamics to model
segment.flight_dynamics.force_x = True
segment.flight_dynamics.force_z = True
# define flight controls
segment.assigned_control_variables.throttle.active = True
segment.assigned_control_variables.throttle.assigned_propulsors = [['starboard_propulsor','port_propulsor']]
segment.assigned_control_variables.body_angle.active = True
mission.append_segment(segment)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
# Descent Segment Flight 1
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
segment = Segments.Climb.Linear_Speed_Constant_Rate(base_segment)
segment.tag = "decent"
segment.analyses.extend( analyses.base )
segment.altitude_start = 8012 * Units.feet
segment.altitude_end = 1000 * Units.feet
segment.air_speed_end = 110 * Units['mph']
segment.climb_rate = -200 * Units['ft/min']
# define flight dynamics to model
segment.flight_dynamics.force_x = True
segment.flight_dynamics.force_z = True
# define flight controls
segment.assigned_control_variables.throttle.active = True
segment.assigned_control_variables.throttle.assigned_propulsors = [['starboard_propulsor','port_propulsor']]
segment.assigned_control_variables.body_angle.active = True
mission.append_segment(segment)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
# Downleg_Altitude Segment Flight 1
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
segment = Segments.Cruise.Constant_Acceleration_Constant_Altitude(base_segment)
segment.tag = 'Downleg'
segment.analyses.extend(analyses.base)
segment.air_speed_end = 45.0 * Units['m/s']
segment.distance = 6000 * Units.feet
segment.acceleration = -0.025 * Units['m/s/s']
segment.descent_rate = 300 * Units['ft/min']
# define flight dynamics to model
segment.flight_dynamics.force_x = True
segment.flight_dynamics.force_z = True
# define flight controls
segment.assigned_control_variables.throttle.active = True
segment.assigned_control_variables.throttle.assigned_propulsors = [['starboard_propulsor','port_propulsor']]
segment.assigned_control_variables.body_angle.active = True
mission.append_segment(segment)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
# Reserve Climb
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
segment = Segments.Climb.Constant_Speed_Constant_Rate(base_segment)
segment.tag = 'Reserve_Climb'
segment.analyses.extend( analyses.base )
segment.altitude_end = 1500 * Units.feet
segment.air_speed = 120 * Units['mph']
segment.climb_rate = 500* Units['ft/min']
# define flight dynamics to model
segment.flight_dynamics.force_x = True
segment.flight_dynamics.force_z = True
# define flight controls
segment.assigned_control_variables.throttle.active = True
segment.assigned_control_variables.throttle.assigned_propulsors = [['starboard_propulsor','port_propulsor']]
segment.assigned_control_variables.body_angle.active = True
mission.append_segment(segment)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
# Researve Cruise Segment
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
segment = Segments.Cruise.Constant_Speed_Constant_Altitude(base_segment)
segment.tag = 'Reserve_Cruise'
segment.analyses.extend(analyses.base)
segment.air_speed = 145* Units['mph']
segment.distance = 60 * Units.miles * 0.1
# define flight dynamics to model
segment.flight_dynamics.force_x = True
segment.flight_dynamics.force_z = True
# define flight controls
segment.assigned_control_variables.throttle.active = True
segment.assigned_control_variables.throttle.assigned_propulsors = [['starboard_propulsor','port_propulsor']]
segment.assigned_control_variables.body_angle.active = True
mission.append_segment(segment)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
# Researve Descent
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
segment = Segments.Descent.Constant_Speed_Constant_Rate(base_segment)
segment.tag = 'Reserve_Descent'
segment.analyses.extend( analyses.base )
segment.altitude_end = 1000 * Units.feet
segment.air_speed = 110 * Units['mph']
segment.descent_rate = 300 * Units['ft/min']
# define flight dynamics to model
segment.flight_dynamics.force_x = True
segment.flight_dynamics.force_z = True
# define flight controls
segment.assigned_control_variables.throttle.active = True
segment.assigned_control_variables.throttle.assigned_propulsors = [['starboard_propulsor','port_propulsor']]
segment.assigned_control_variables.body_angle.active = True
mission.append_segment(segment)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
# Baseleg Segment Flight 1
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
segment = Segments.Climb.Linear_Speed_Constant_Rate(base_segment)
segment.tag = 'Baseleg'
segment.analyses.extend( analyses.base)
segment.altitude_start = 1000 * Units.feet
segment.altitude_end = 500.0 * Units.feet
segment.air_speed_start = 45
segment.air_speed_end = 40
segment.climb_rate = -350 * Units['ft/min']
# define flight dynamics to model
segment.flight_dynamics.force_x = True
segment.flight_dynamics.force_z = True
# define flight controls
segment.assigned_control_variables.throttle.active = True
segment.assigned_control_variables.throttle.assigned_propulsors = [['starboard_propulsor','port_propulsor']]
segment.assigned_control_variables.body_angle.active = True
mission.append_segment(segment)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
# Final Approach Segment Flight 1
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
segment = Segments.Climb.Linear_Speed_Constant_Rate(base_segment)
segment_name = 'Final_Approach'
segment.tag = segment_name
segment.analyses.extend( analyses.base)
segment.altitude_start = 500.0 * Units.feet
segment.altitude_end = 00.0 * Units.feet
segment.air_speed_start = 40
segment.air_speed_end = 35
segment.climb_rate = -300 * Units['ft/min']
# define flight dynamics to model
segment.flight_dynamics.force_x = True
segment.flight_dynamics.force_z = True
# define flight controls
segment.assigned_control_variables.throttle.active = True
segment.assigned_control_variables.throttle.assigned_propulsors = [['starboard_propulsor','port_propulsor']]
segment.assigned_control_variables.body_angle.active = True
mission.append_segment(segment)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
# Mission definition complete
# ------------------------------------------------------------------
return mission
Missions Setup#
The missions_setup function is responsible for setting up a list of missions. This allows multiple missions to be incorporated if desired, but only one is used here.
Initialize Missions Object: It creates an empty
Missionsobject from theRCAIDE.Framework.Missionmodule.Tag the Mission: It assigns the tag
'base_mission'to the providedmissionobject. This tag is used to identify the mission.Add Mission to List: It adds the tagged
missionto theMissionsobject.Return Missions Object: Finally, it returns the
Missionsobject, which now contains the tagged mission.
[7]:
def missions_setup(mission):
missions = RCAIDE.Framework.Mission.Missions()
# base mission
mission.tag = 'base_mission'
missions.append(mission)
return missions
Plot Mission#
The last function in this file is used to plot the performance results from the mission evaluation. The results shown are not an exhaustive list of RCAIDE outputs, and custom plotting routines can be created.
[8]:
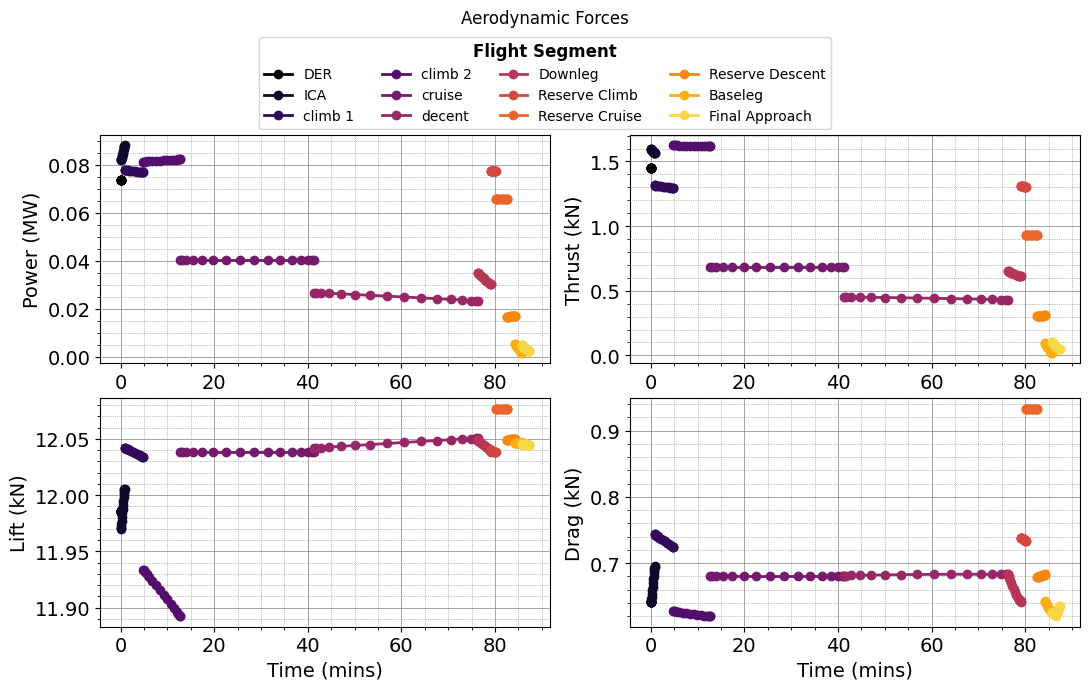
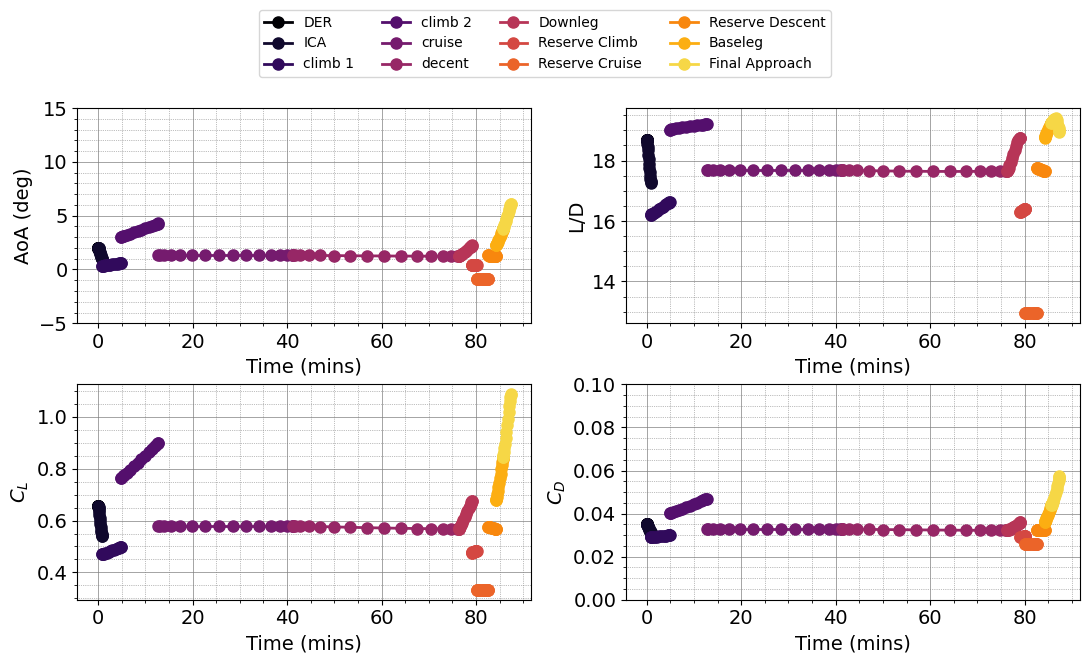
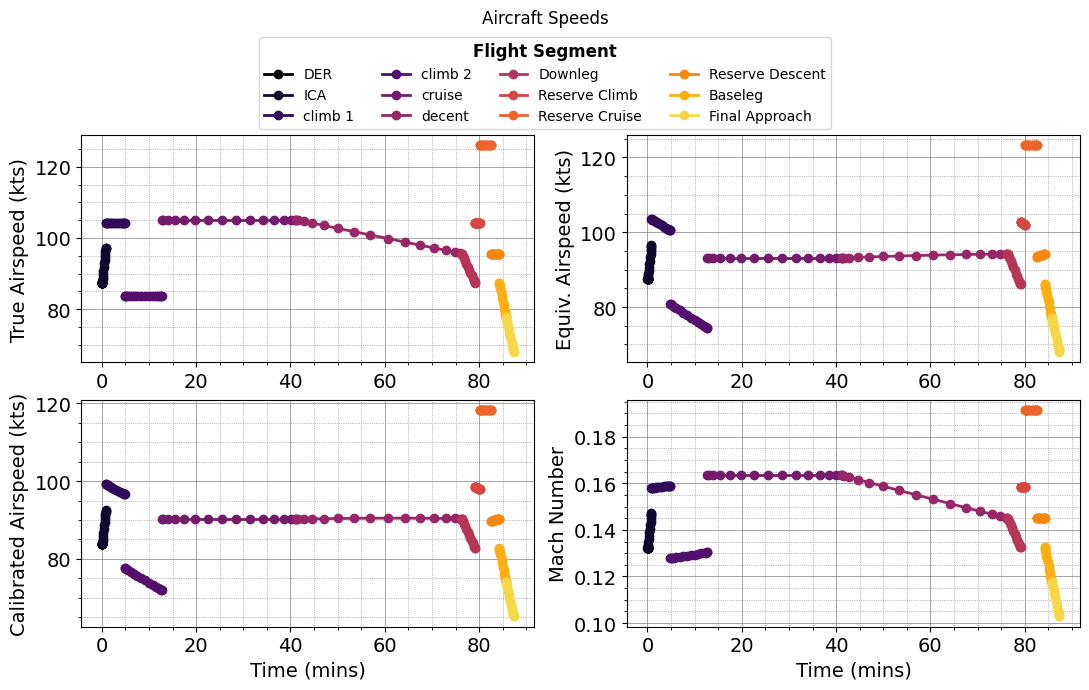
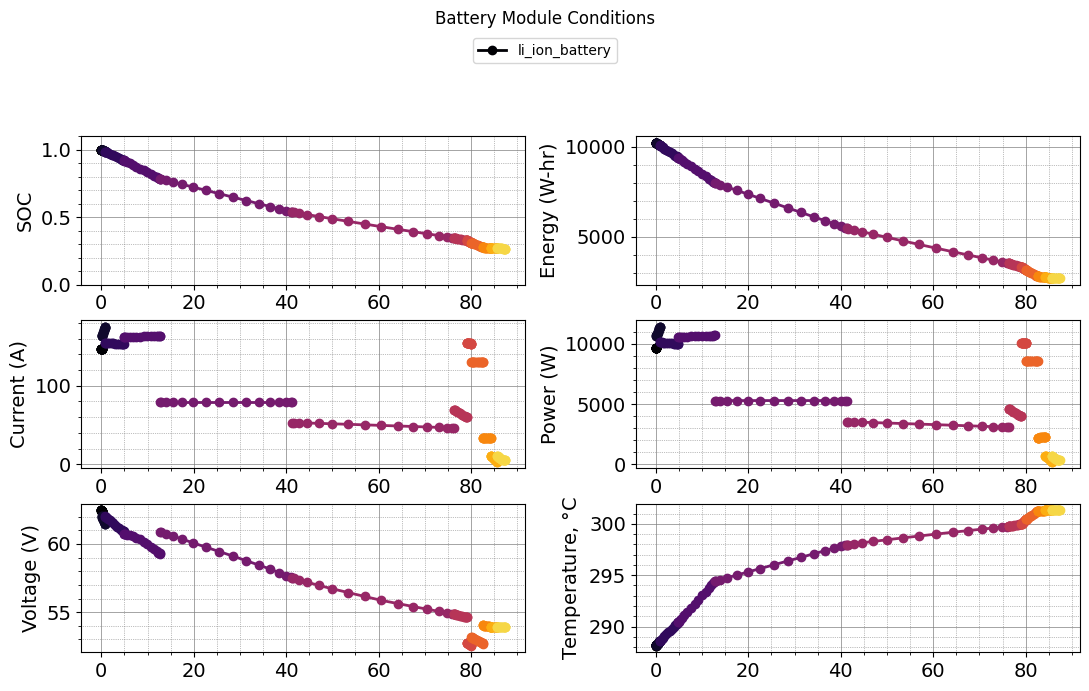
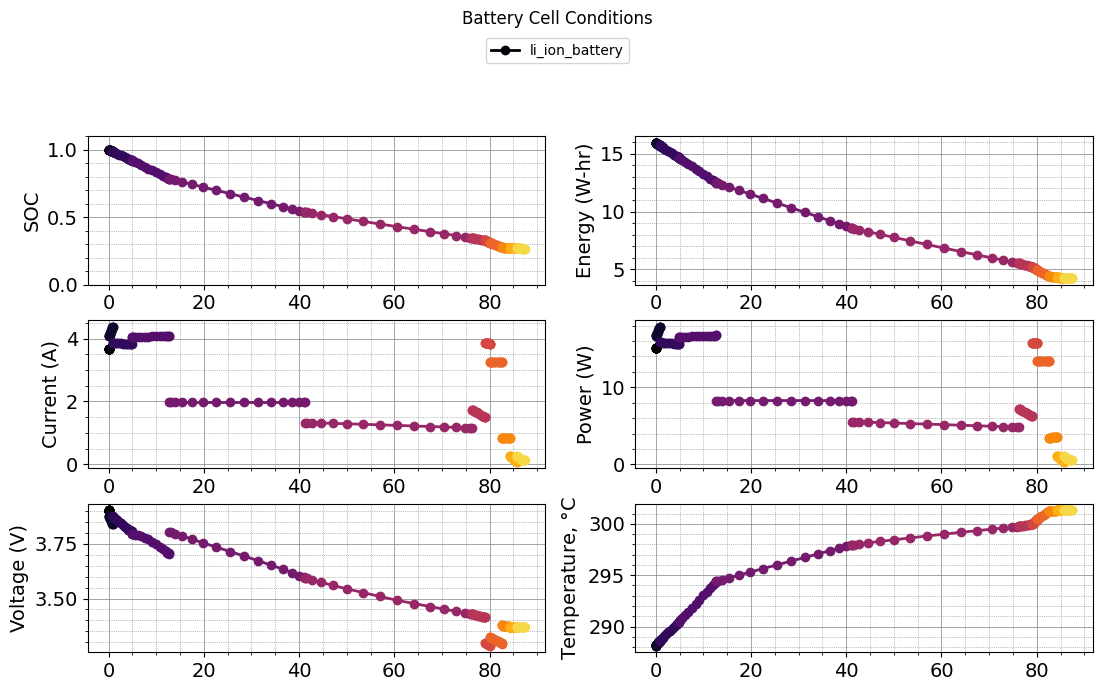
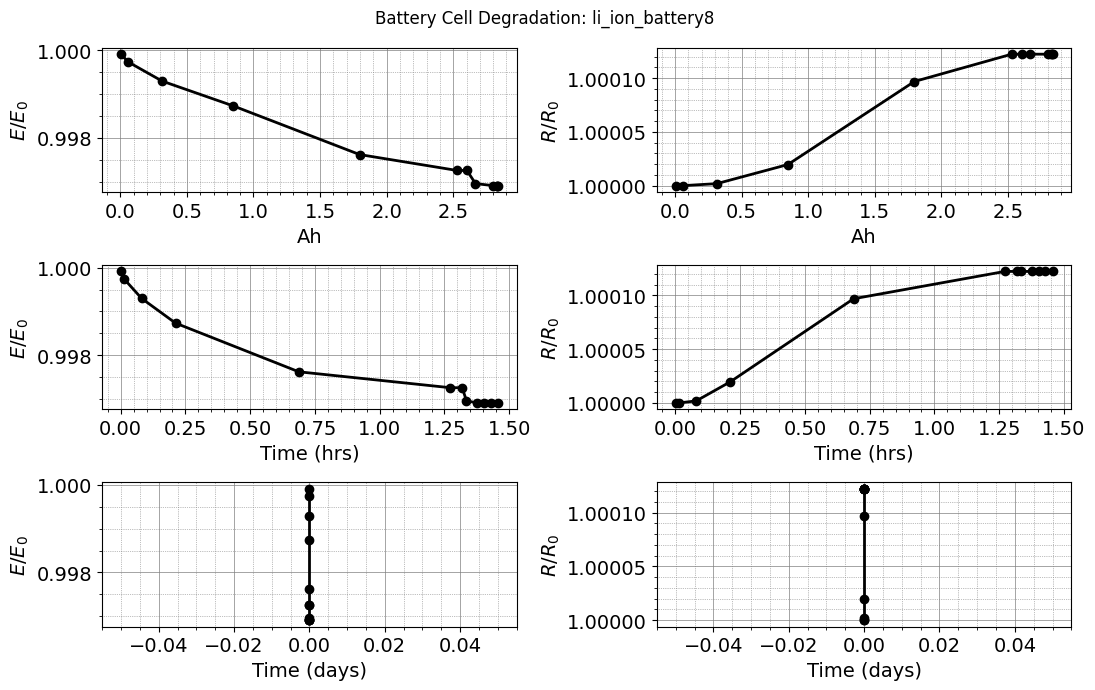
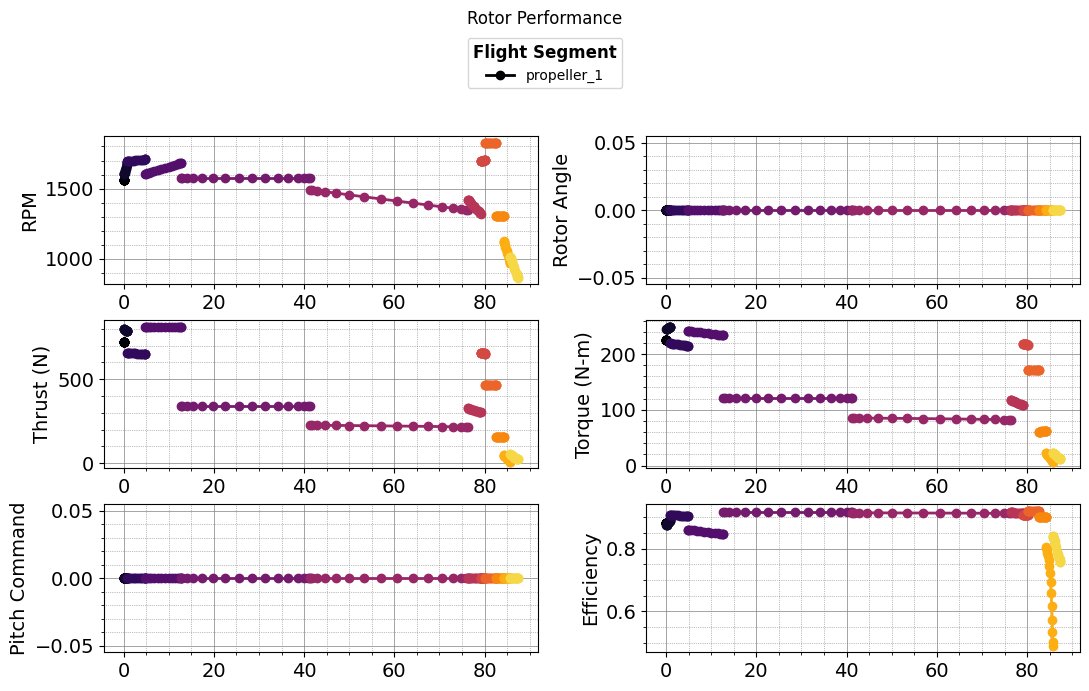
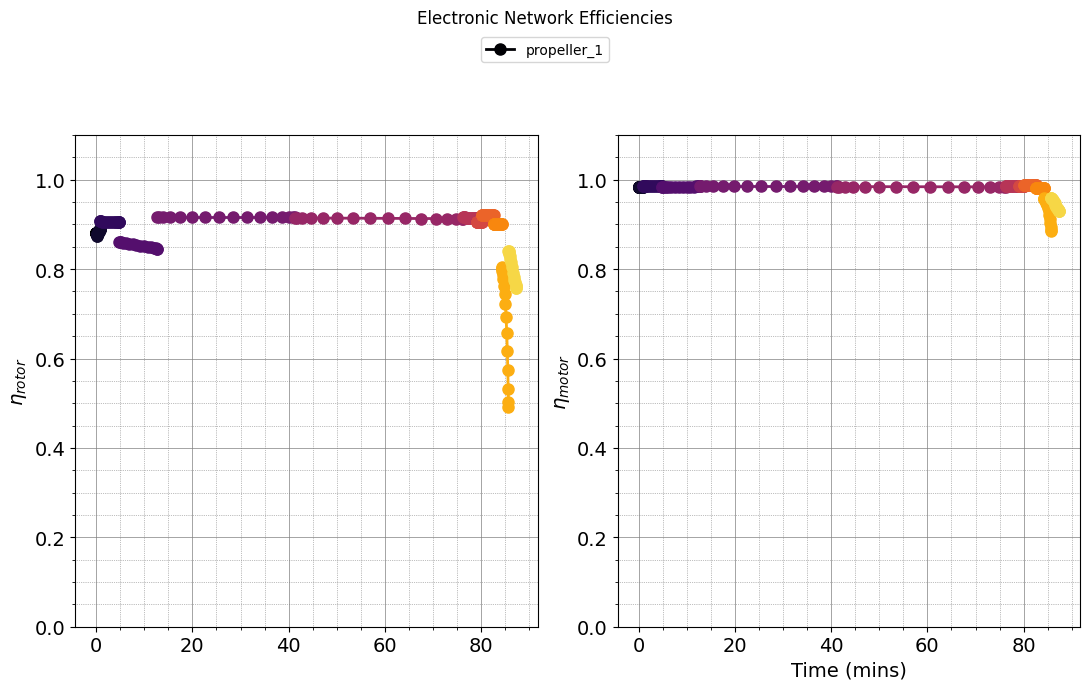
def plot_mission(results):
plot_flight_conditions(results)
plot_aerodynamic_forces(results)
plot_aerodynamic_coefficients(results)
plot_aircraft_velocities(results)
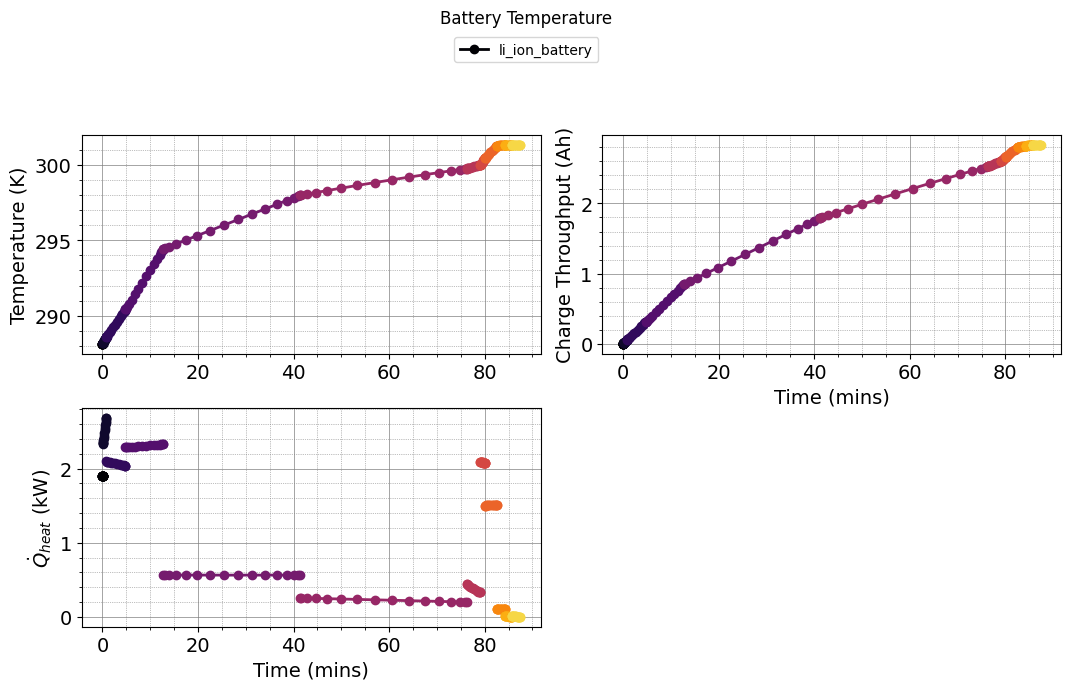
plot_battery_module_conditions(results)
plot_battery_cell_conditions(results)
plot_battery_degradation(results)
plot_rotor_conditions(results)
plot_electric_propulsor_efficiencies(results)
plot_battery_temperature(results)
return
Main Script#
The main script is used to call each of the functions defined above to execute the mission. A main script is used to run the functions for increased readability and maintainability.
[9]:
# vehicle data
vehicle = vehicle_setup()
# Set up vehicle configs
configs = configs_setup(vehicle)
# create analyses
analyses = analyses_setup(configs)
# mission analyses
mission = mission_setup(analyses)
# create mission instances (for multiple types of missions)
missions = missions_setup(mission)
# mission analysis
results = missions.base_mission.evaluate()
# plot the results
plot_mission(results)
# plot vehicle
plot_3d_vehicle(configs.base,
min_x_axis_limit = 0,
max_x_axis_limit = 40,
min_y_axis_limit = -20,
max_y_axis_limit = 20,
min_z_axis_limit = -20,
max_z_axis_limit = 20)
Performing Weights Analysis
--------------------------------------------------------
Propulsion Architecture: Electric
Aircraft Type : General_Aviation
Method : Physics_Based
Aircraft operating empty weight will be overwritten
Aircraft center of gravity location will be overwritten
Aircraft moment of intertia tensor will be overwritten
Mission Solver Initiated
0%| | 0/100 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Solving DER segment.
108it [11:13, 6.24s/it]
Solving ICA segment.
Solving climb_1 segment.
Solving climb_2 segment.
Solving cruise segment.
Solving decent segment.
Solving Downleg segment.
Solving Reserve_Climb segment.
Solving Reserve_Cruise segment.
Solving Reserve_Descent segment.
Solving Baseleg segment.
Solving Final_Approach segment.
Plotting vehicle